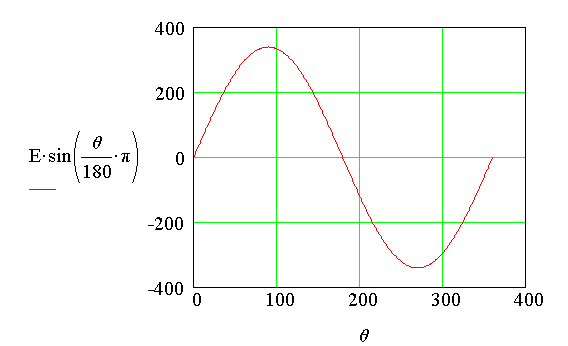

E = 340 V
R = 10 W
wL = 2 x p x 50 x 31.8 x 10-3 W
a = atan (wL/R)
a = 0.785 rad
The value of L is set to be 31.8 mH. The frequency is set to be 50 Hz. The load angle is calculated for the specified values of R, L and f.
Z = 14.135 W
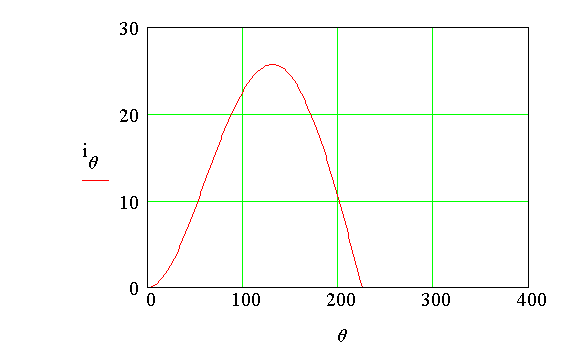
A = 17 Amp
The value of the coefficient A has been computed. Now
the plots of the source voltage, the current thr ough
the diode and the voltage at the cathode of
diode are obtained. A range variable, called q,
is created first and it is varied from 0 deg to 360
deg. At each degree, the current through
the diode is computed.
The expression for current, Curq
, shown above would yield positive values if
q is less than the conduction angle and would
yield negative values if q
is higher than the conduction angle. The statement below creates an
array called iq and
it is set equal to Curq , if Curq
is positive. If Curq
is negative, iq is
set equal to zero. The expression within the brackets is similar
to arithmetic IF operator in C language. Given
x :=if (expr1,expr2, expr3 ),
x is assigned the value of expr2, if expr1 evalautes to
Boolean TRUE value and x is assigned the value
of expr3, if expr1 evalautes to Boolean FALSE value. This arithmetic IF
operation is carried out for each value of array
iq taking into account
the corresponding value of Curq . That
is, both iq and Curq
have the same index, q when evaluation
is performed.
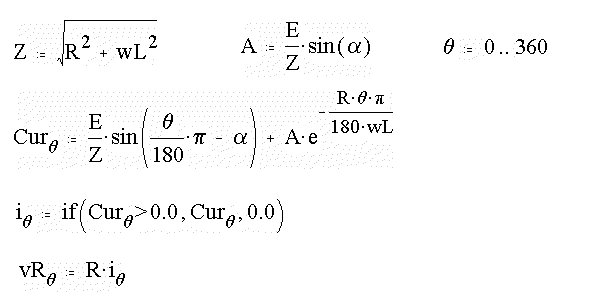
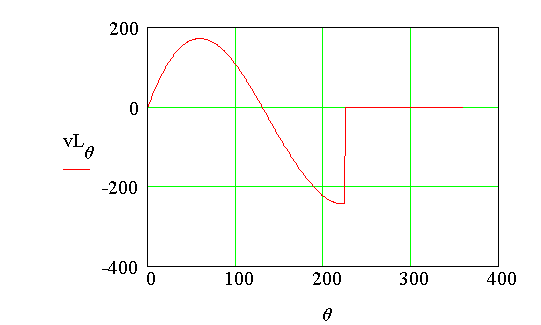
The voltage across the resistor can be computed as shown below. Next the voltage across the inductor is computed. Again the arithemtic IF operation is carried out. When the diode current is positve, the voltage across the inductor is the difference between the source voltage and the voltage across the resistor. When the diode current is zero, the voltage across the inductor is also zero. Next the conduction angle is determined. MathCad allows a particular construct. Assign a guess value for conduction angle. Here it is called b and is assigned a value of p radians. Next form a block staring with Given statement. The equality that should exist is presented below. The program then evaluates the correct value of b for which the equality is true. Then that value of b is assigned to another variable called d in this program.
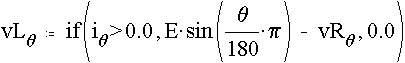
b := p
Given
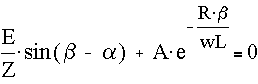
d := Find(b)
d = 3.94 rad
When wt = d,
the current through the load becomes zero. The dc value of this current
is found out as shown below. Here this current is
expressed as a function of x and this function is integrated
over
the period
of conduction.
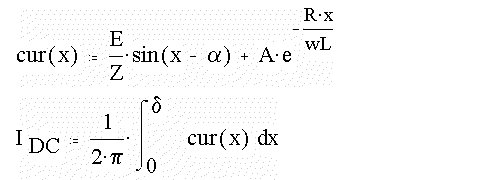
IDC = 9.187 Amp
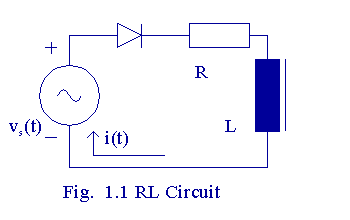
The ac source shown in Fig. 1.1
has to supply this dc current. An ac source should not normally be
required to supply a dc current. The mains
ac supply is distributed using transformers and a transformer
is not designed to supply a dc current. It is
preferable to avoid using half-wave rectifier circuits.